Material Testing
ADACS offers customers well designed test programs for material characterization at a range of temperatures, and strain rates. Along with our testing partners, we can design and execute a full test program for your material.
Material testing and characterization services include,
- sample machining, preparation, and inspection
- measurement of thermal and physical properties
- measurement of elastic coefficients
- measurement of monotonic and cyclical properties
- measurement of viscous properties
- determination of isothermal fatigue properties
- determination of Thermo-Mechanical Fatigue properties
- Determination of HCF on LCF life properties
- Determination of HCF on TMF life properties
Typical test Program: 60-400 specimens, 8 temperatures, 3-4 months turnaround (after receipt of samples)
Extensive testing experience with the following material classes:
- SiMo Irons
- Cast Irons
- Cast Aluminum
- Cast Stainless Steel
- Superalloys
Not only metals but also plastics and other materials.
Data is provided in reduced as well as raw formats.
In addition, material parameters for various constitutive models can be provided for FEA. Moreover, stress-life, strain-life, and TMF model parameters would be computed using optimization algorithms.

Constitutive Modeling
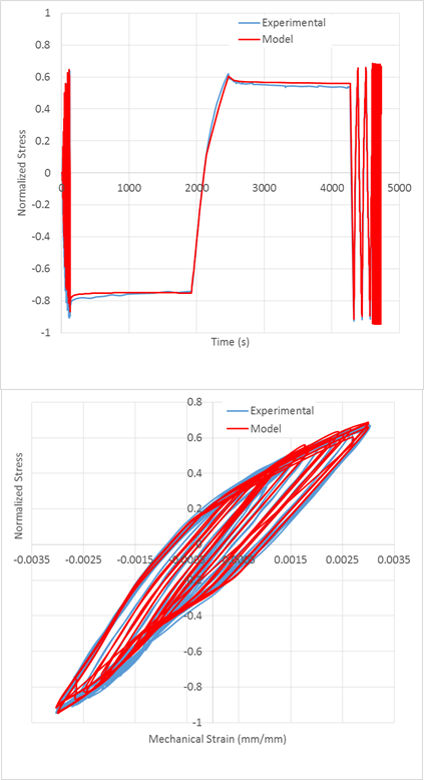
ADACS offers a wide range of robust constitutive models based on the unified Chaboche as well as other advanced constitutive models (e.g. Cast Iron Plasticity). These can be easily integrated into commercial FEA packages. The models are intended to capture important material behavior effects, e.g.
– Cyclical hardening and softening
– Kinematic harening
– Strain rate effects
– “Creep-plasticity” interaction
– Static and dynamic recovery
– Material aging
– Tension-compression asymmetry with damage for Cast-Iron
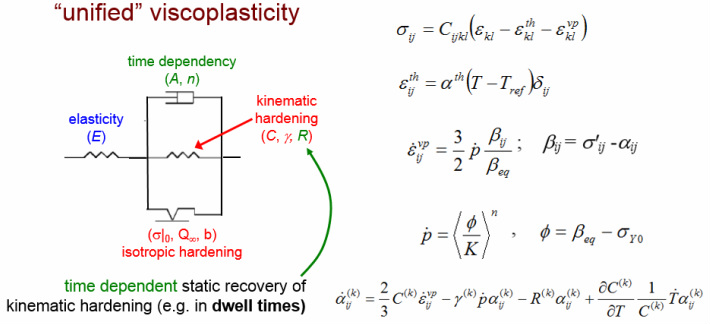
UMAT
At ADACS, we have developed a User Material model for simulating the behavior of Cast Iron. This material exhibits an anisotropic behavior between tension and compression. The asymmetric tension/compression behavior has been characterized including non linear kinematic hardening, strain rate effect, damage leading to modulus degradation, asymmetric behavior (tensile vs compression).
This 1D version of this model is implemented in the simulation code SiDoLo. It also allows the identification of the material parameters.The 3D versions are implemented as a UMAT in the Abaqus Software and as a usermat in the Ansys Software with modular number of temperatures and kinematic variables.
The degradation of the material is accounted for using a brittle damage type. The fatigue damage is computed incrementally depending on the stress state.
A second procedure based on skip cycles calculating the fatigue damage as function of the total energy is also implemented.